|
Common Name |
Honey Fungus |
Honey Fungus 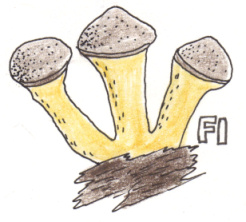
F1 Honey Fungus Fruiting
|
Scientific Name
|
Armillariella melloea
|
Physical Description
|
Fruits arise in July, Dececember. Caps are 15cm in clusters on stem and trunk. Yellow or tawny colour. Dark specks seen. Gills white.
|
Habitat
|
Mycelium lives in soil. Common in gardens, and old stumps.
|
Life Cycle
|
Saprophytic mycelium enters tree, and usually stays on roots, until tree is diseased, then attacks and kills tree. Spores produced from fruiting bodies.
|
Damage Caused
|
Wood becomes stained and wet. Rot in heartwood. Usually confined to roots until tree dies. Mycelium looking like boot lace strands seen in trees. Young trees may be killed. May lead to wind drop.
|
Control Method
|
Difficult. Remove trees at first signs, remove and replace soil. Remove hazardous trees. On infected sites plant Ash, Box, Acacia, Hawthorn, Ivy, Larch, Laurel, Lime, Mahonia, Fir, Yew. Remove all dead wood.
|
Plants Affected
|
Apples, Birch, Cedar, Cypress, Lilac, Pine, Privet, Willow.
|
Life Cycle
|
Difficult. Hygiene with tools, remove dead litter and branches. Uproot the diseased. |
Information Collated by James M. Burton as part of H.N.D. Course at Pencoed Agricultural College.
Chemical Information Correct as of 06:06:97. Always read and follow the instructions when using fungicides.